What Do Welders Do?
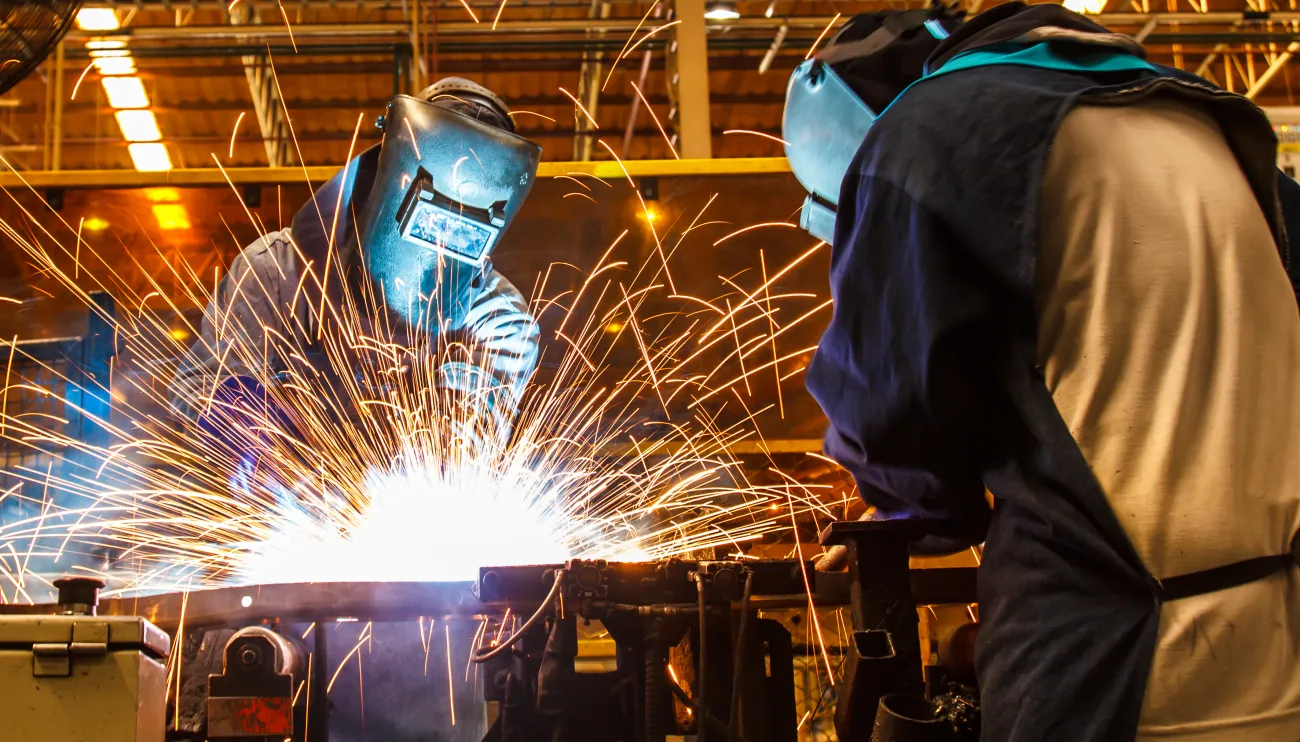

Responsibilities
From getting comfortable with blueprint creation to using heavy machinery, welders have a wide range of responsibilities. Those include:
- Study and interpret blueprints and measurements
- Read sketches and specifications
- Inspect structures and materials before welding
- Operate torches and power supplies
- Use and maintain specialized welding machines and equipment
- Weld components
- Monitor stages of the welding process
- Assess the quality of welds and identify flaws
- Follow strict safety regulations – including wearing the right safety gear
How To Become a Welder: FAQs
The bottom line:
You can expect to choose from a variety of different types of welding. In fact, there are more than 100 welding processes. Working in a field like welding, you’ll often find yourself outdoors in all kinds of weather – sometimes on a scaffold or a platform off the ground. Some of the jobs you’ll do might include gas metal arc or gas tungsten arc welding, flux core welding or shielded metal arc welding for structural jobs.
Once you’re on the path to becoming a certified welder, the sky’s the limit. If you like working outside, you might consider specializing in one of the areas of welding that will allow you to do that. An exciting career in construction, aircraft or maritime welding will give you an area of expertise.
As a welder in engineering construction, you’ll work on buildings, dams, water supply systems, bridge applications and more. This rapidly changing industry has seen innovative developments in the last decade, and your skills and craftsmanship will be critical to success. You’ll help to build the structures that serve communities across the country and encounter new technologies like laser-arc hybrid welding and friction techniques in your work.
As an aircraft welder, you’ll get to use different welding techniques in the manufacture and repair of jets, commercial airplanes and helicopters, including SMAW, MIG and TIG welding. Aircraft fabrication technologies have evolved over the years to include lighter metals, such as titanium and magnesium. To get qualified for this job, enroll in a training program out of high school, and learn processes commonly used in the aircraft industry.
Maritime welding requires specialist skills and knowledge. You’ll connect metals or plastics to produce joints that are water- and oil-tight. If you’re interested in this area, you should look to train in aluminum, structural and pipe welding. You should also seek out programs that include safety and standards procedures for shipyards.
Welding is a great career that allows you to develop skills and find new ways to assert yourself. It’s work that not only serves you, but also positively affects your community.
Why becoming a welder is worthwhile
"When I first started, I just needed a job," says Travis Edmonds. "But now that I've been here 17 years, it's more than just that. I found myself, I found a career."
Travis loves being a welder because there are so many different things you can do once you learn the skill. It's a career that has taken him all over the U.S. and even the world. He's always looking for new challenges — and welding keeps on providing them.
On top of that, it's fun. "If you get bored in welding, you're doing something wrong."
Want another insider's view? Vince McGill says when he started welding, it was just a job — but it quickly turned into a career.
Are there certification requirements for this career?
Find Welder Training In Your Area
Need help reaching your goals?
Explore our Financial Resources page for scholarships, FAQ answers and student support services.

